Howdy
h1>
The Importance of High Voltage Testing for Electrical
In industrial, commercial, and even certain residential electrical systems, safety and reliability are non-negotiable. High voltage testing is an essential but frequently overlooked component of verifying both. A high voltage tester can be used to check the quality of the insulation, find problems before they become harmful, and ensure that safety standards are being followed.
This article will explore why high voltage testing matters, how it works, and best practices for using a high voltage tester to keep your electrical equipment safe and operational.
What Is a High Voltage Tester?
A high voltage tester is a specialized device used to apply a controlled high voltage to electrical equipment or components to assess their insulation quality and performance under stress. The purpose is to ensure that the equipment can handle voltages higher than its normal operating level without failing.
These testers are commonly used in:
- Electrical manufacturing
- Power distribution systems
- Maintenance of transformers, cables, and switchgear
- Quality control for electrical products
By simulating extreme conditions, a high voltage tester helps uncover hidden weaknesses before they cause breakdowns or safety hazards.

Why Regular High Voltage Testing Is Critical
Electrical insulation degrades over time due to environmental factors, mechanical stress, and regular wear and tear. Without regular testing, you may not realize there’s a problem until it’s too late. Here’s why consistent high voltage testing is so important:
1. Preventing Electrical Failures
Insulation breakdown can lead to short circuits, equipment damage, or even fires. Regular testing ensures potential faults are detected early, reducing costly downtime.
2. Ensuring Safety for Personnel
Electrical faults can pose serious hazards to workers. A well-maintained high voltage tester identifies issues before they put lives at risk.
3. Meeting Industry Standards
Many industries require periodic high voltage testing to comply with safety regulations and standards such as IEEE, IEC, or OSHA guidelines.
4. Prolonging Equipment Lifespan
By catching problems early, you can repair or replace components before they cause damage to the entire system, extending the life of your electrical assets.
5. Improving System Reliability
A single failure in a high-voltage system can halt operations. Testing minimizes unplanned outages and keeps your system running smoothly.
How High Voltage Testing Works
High voltage testing involves applying a higher-than-normal voltage to the equipment under controlled conditions. A high voltage tester then monitors the system to see if there is any breakdown or leakage current.
There are two primary types of high voltage tests:
1. AC High Voltage Test
Uses alternating current to check insulation performance under normal operating conditions. It is ideal for equipment that runs on AC systems.
2. DC High Voltage Test
Uses direct current to test insulation, often used for long cables and certain types of electrical components because it provides stable readings over time.
The test parameters, such as voltage level and duration, depend on the equipment type, its rating, and relevant industry standards.
When Should You Perform High Voltage Testing?
To maintain safety and reliability, high voltage testing should be part of a regular maintenance schedule. Common situations where a high voltage tester is used include:
- Before commissioning new equipment to ensure it meets design specifications.
- After repairs or modifications to confirm equipment is still safe to operate.
- During scheduled maintenance intervals as per manufacturer or regulatory guidelines.
- Following unusual operating conditions such as lightning strikes, power surges, or floods.
For critical infrastructure, some facilities test equipment annually, while others do so every few years depending on usage and environmental factors.
Benefits of Using a High Voltage Tester Regularly
1. Early Detection of Problems
A high voltage tester can reveal issues like moisture ingress, insulation cracks, or aging materials that aren’t visible during a standard visual inspection.
2. Reduced Downtime and Costs
By addressing problems early, you avoid expensive emergency repairs and production losses from unexpected outages.
3. Increased Safety Compliance
Passing high voltage tests ensures your equipment meets local and international safety standards, protecting you from legal or regulatory issues.
4. Data-Driven Maintenance
Modern high voltage testers often store historical test data, helping maintenance teams track performance trends and make proactive decisions.
Best Practices for High Voltage Testing
To get accurate and safe results when using a high voltage tester, follow these best practices:
- Understand Equipment Specifications – Always check the manufacturer’s voltage rating before testing.
- Follow Standard Procedures – Use test methods that align with recognized standards like IEC 60060 or IEEE 4.
- Use the Right Tester – Choose a tester that matches your application (AC, DC, portable, or laboratory-grade).
- Ensure Proper Grounding – Good grounding is critical to prevent accidents during testing.
- Wear Appropriate PPE – High voltage testing is dangerous; use insulating gloves, safety glasses, and other personal protective equipment.
- Document Test Results – Keep detailed records for compliance, trend analysis, and maintenance planning.
Safety Precautions When Using a High Voltage Tester
High voltage testing involves significant electrical hazards. Always prioritize safety:
- Isolate the equipment from the power supply before testing.
- Ensure only trained personnel operate the tester.
- Maintain a safe distance and use insulated tools.
- Keep bystanders away from the test area.
- Never exceed the recommended voltage limits.
A high voltage tester is a powerful diagnostic tool, but it can be dangerous if used improperly.
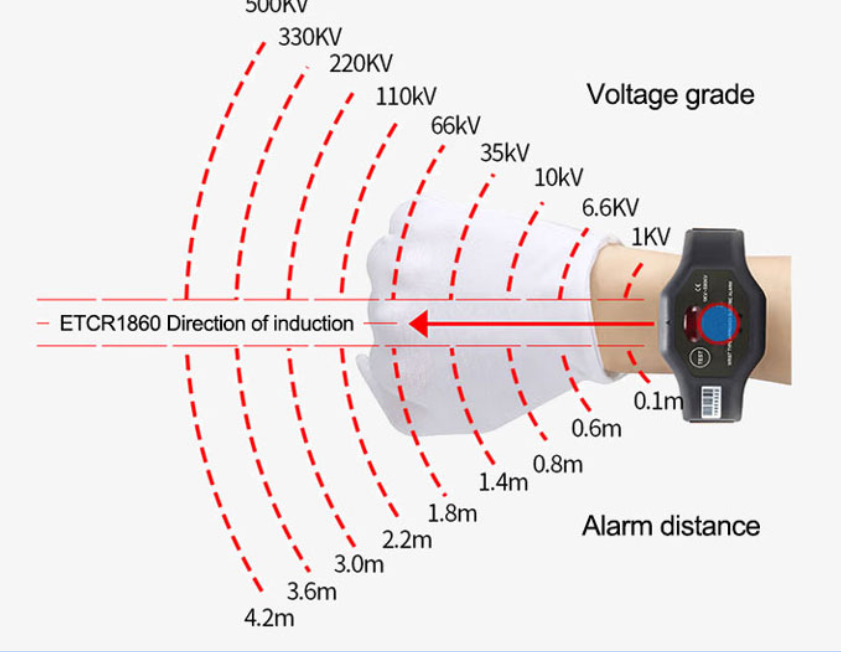
Choosing the Right High Voltage Tester
When selecting a high voltage tester, consider the following:
- Voltage Range – Ensure it covers your testing needs.
- Portability – Field technicians may prefer lightweight arm type or wrist type, while labs may use larger, more advanced units.
- Display and Controls – Clear readings and simple controls improve accuracy and ease of use.
- Safety Features – Look for built-in grounding, emergency shut-off, and overvoltage protection.
- Data Logging – Useful for tracking historical performance and generating maintenance reports.
Real-World Example of High Voltage Testing Benefits
Consider a manufacturing plant operating high-voltage motors. During routine testing with a high voltage tester, the maintenance team detects insulation degradation in one motor. By repairing it promptly, they prevent a costly failure that could have halted production for days, saving both money and time.
This example shows how preventive maintenance using high voltage testing can directly impact productivity and profitability.
Conclusion
The high voltage testing is not just a technical requirement, but it’s a vital part of maintaining safe, efficient, and reliable electrical systems. A high voltage tester enables early fault detection, extends equipment lifespan, ensures compliance, and ultimately saves time and money.
Whether you’re overseeing industrial machinery, power distribution equipment, or electrical components in a laboratory setting, making high voltage testing a routine practice is one of the smartest investments you can make in operational safety and efficiency.



